Markers of oxidative stress in erythrocytes and plasma during aging in humans.
Pandey KB, Rizvi SI -Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity(2010 Jan-Feb)
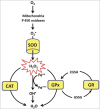
F5:Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR) and catalase (CAT) are the main endogenous enzymatic defense systems of all aerobic cells. They give protection by directly scavenging superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide, converting them to less reactive species. SOD catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide radical (•O2) to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Although H2O2 is not a radical, it is rapidly converted by fenton reaction into •OH radical which is very reactive. GPx neutralizes hydrogen peroxide by taking hydrogens from two GSH molecules resulting in two H2O and one GSSG. GR then regenerates GSH from GSSG. CAT the important part of enzymatic defense, neutralizes H2O2 into H2O.
View Article:PubMed Central - PubMed
Affiliation:Department of Biochemistry, University of Allahabad, Allahabad, India.
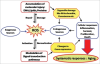
Bottom Line:Aging is an inevitable universal biological process, which can be characterized by a general decline in physiological function with the accumulation of diverse adverse changes and increased probability of death.Among several theories, oxidative stress/free radical theory offers the best mechanistic elucidation of the aging process and other age -related phenomenon.In the present paper , we discuss the aging process and have focused on the importance of some reliable markers of oxidative stress which may be used as biomarkers of the aging process.
Abstract
Aging is an inevitable universal biological process, which can be characterized by a general decline in physiological function with the accumulation of diverse adverse changes and increased probability of death. Among several theories, oxidative stress/free radical theory offers the best mechanistic elucidation of the aging process and other age -related phenomenon. In the present paper , we discuss the aging process and have focused on the importance of some reliable markers of oxidative stress which may be used as biomarkers of the aging process.
Mentions
Several enzymes have evolved in aerobic cells to overcome the damaging effects of ROS. They are significantly used to maintain the redox balance during oxidative stress and are collectively called as endogenous antioxidative enzymes. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR) and catalase (CAT) are the main endogenous enzymatic defense systems of all aerobic cells.4,91 They give protection by directly scavenging superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide, converting them to less reactive species (Fig. 5).92 SOD catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide radical (•O2) to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Although H2O2 is not a radical, it is rapidly converted by fenton reaction into •OH radical which is very reactive. Among various antioxidant mechanisms in the body, SOD is thought to be one of the major enzymes that protect cells from ROS. The liver, in particular, is very high in SOD. Cellular concentration of SOD relative to metabolic activity is a very good lifespan predictor of animal species. Most mammals experience a lifetime energy expenditure of 200,000 calories per gram, but humans have an amazing 800,000 calories per gram.93 Humans have the highest levels of SOD relative to metabolic rate of all species studied. Oxidative damage to DNA is ten times greater in rats than in humans. Maximum lifespan correlates with lower rate of free-radical production and higher rate of DNA repair.93
MeSH
Major
Aging/metabolism*/physiology*
Biomarkers/metabolism*
Erythrocytes/metabolism*
Oxidative Stress/physiology*
Minor
Humans
Models, Biological